Spring Boot在Sping MVC基础上,实现了"0"配置运行Spring项目,那他是如何实现的呢,原理其实很简单,在Tomcat、Servlet、Spring、SpringMVC发展过程中,都逐步实现了通过Java代码运行,而不需要任何配置,Spring Boot就是把整个过程通过代码实现了;自己也可以通过代码一步步实现,下面是官方介绍。
Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that you can “just run”.
We take an opinionated view of the Spring platform and third-party libraries so you can get started with minimum fuss. Most Spring Boot applications need minimal Spring configuration.
构建Tomcat容器
通过官方介绍,Spring Boot基于SpringMVC、Spring MVC则是在Servlet基础上,Servlet一般运行与Tomcat容器中;如果实现SpringBoot,就要用纯代码方式实现Tomcat容器,而不依赖外部。先要创建Java项目通过代码实现Tomcat容器,方法就是引入相关tomcat jar包,通过maven更简单:
|
|
接下来简单几句话实现Tomcat容器运行;这样完全可以在调试阶段替代掉IDE中的Tomcat插件或者tomcat容器了,命令行或者maven就可以运行了;so easy!
|
|
通过APP.main()方法运行项目,访问:http://localhost:8081/, 发现端口监听可以了,不过现在还没有Servlet,接下来实现一个简单Servlet:
实现Servlet
|
|
之前Servlet要想访问,都是web.xml文件中配置Servlet,Spring Boot既然不用xml文件,那怎么注册?在Servlet3.0之后,新增ServletContainerInitializer接口实现免web.xml配置:
- ServletContainerInitializer接口的实现类通过java SPI声明自己是ServletContainerInitializer 的provider.
- 容器启动阶段依据java spi获取到所有ServletContainerInitializer的实现类,然后执行其onStartup方法.
- 另外在实现ServletContainerInitializer时还可以通过@HandlesTypes注解定义本实现类希望处理的类型,容器会将当前应用中所有这一类型(继承或者实现)的类放在ServletContainerInitializer接口的集合参数c中传递进来。如果不定义处理类型,或者应用中不存在相应的实现类,则集合参数c为空.
- 这一类实现了 SCI 的接口,如果做为独立的包发布,在打包时,会在JAR 文件的 META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer 文件中进行注册。 容器在启动时,就会扫描所有带有这些注册信息的类(@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)这里就是加载WebApplicationInitializer.class类)进行解析,启动时会调用其 onStartup方法——也就是说servlet容器负责加载这些指定类, 而ServletContainerInitializer的实现者(例如Spring-web中的SpringServletContainerInitializer对接口ServletContainerInitializer的实现中,是可以直接获取到这些类的)
1、创建ServletContainerInitializer实现类,并注册Servlet,或者另外配置@HandlesTypes:
|
|
2、SPI声明,供tomcat库调用创建文件:
文件中写入类名全路径:
|
|
再次运行项目访问:http://localhost:8081/hello 成功访问到Servlet。
集成Spring MVC 实现 Spring Boot
最后集成Spring MVC就算初步成功了。实际上SpringMVC中就是通过该方式配置的,在Srping-web的jar包中可以找到该文件, 在理解了Java Servlet Web 代码构建后,下一步我们代码构建Spring MVC, 在spring的官方文档中,推荐的就是代码集成:
|
|
分析代码就能发现,其实做了两件事,注册配置类(AppConfig.class)、注册DispatcherServlet;这不就是Spring MVC在web.xml中做的事情吗,另外该类就是通过实现ServletContainerInitializer时Springweb源码中配置了@HandlesTypes,则,调用了该类:
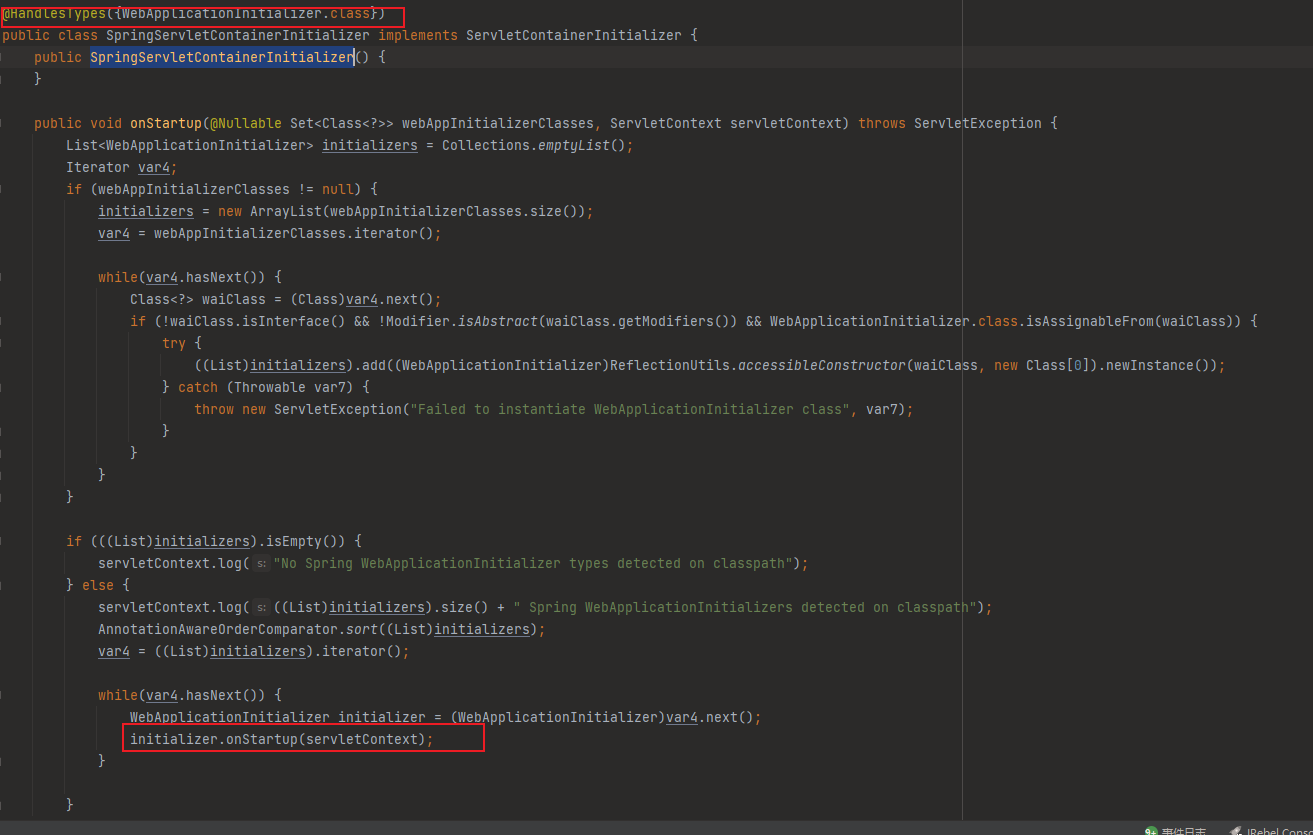
上面代码中的AppConfig就是Spring MVC的配置文件,配置ComponentScan,bean注册、以及其它配置:
|
|
到这我们就可以愉快的写Controller
|
|
访问http://localhost:8081/app/index,就能访问controller。
最后整个过程没有用xml,实现从main方法启动,这不就是最基本的SpringBoot的启动原理吗,当然,SpringBoot最强大的地方在于他和各种框架的无xml集成,只要在有相关jar包引入,则自动配置,基本原理也很简单,就是用了SPI标准。
源码地址:git@github.com:shanyutou/custom-boot.git
